Where Do Builders and Remodelers Buy Building Products?
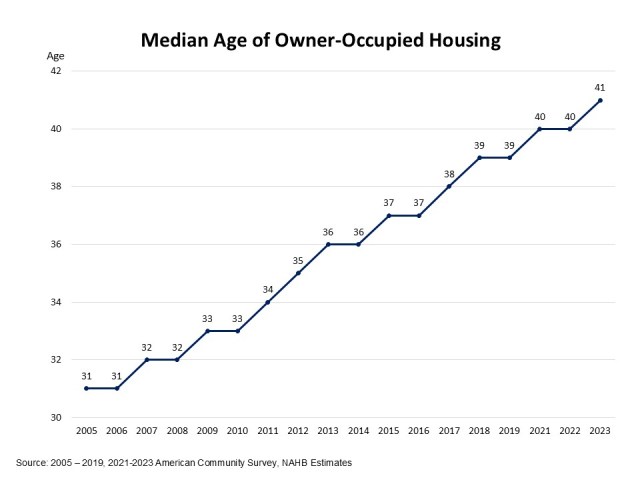
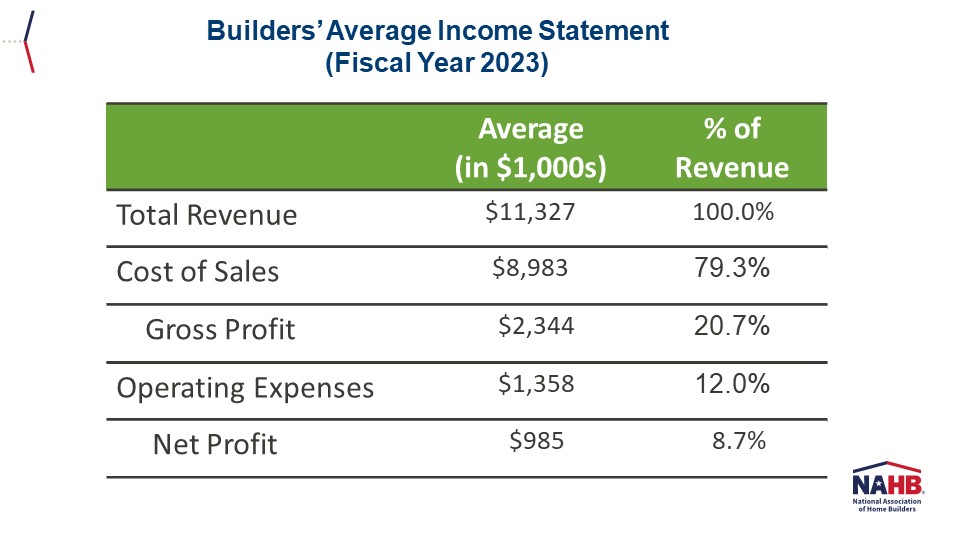
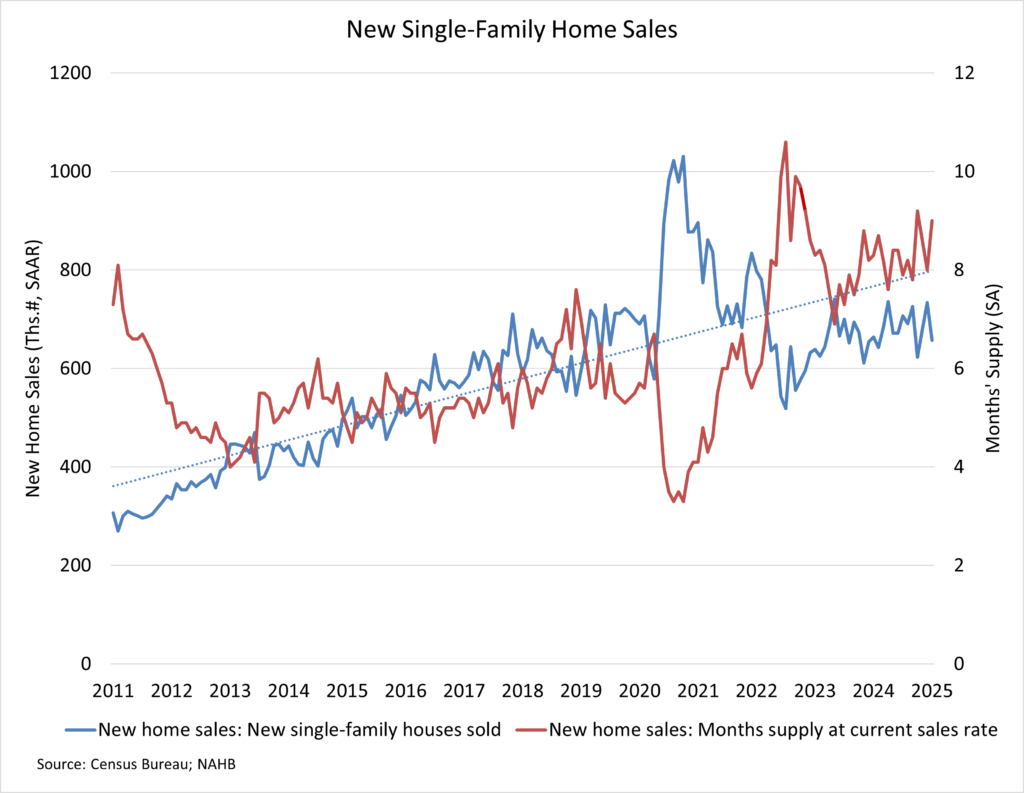
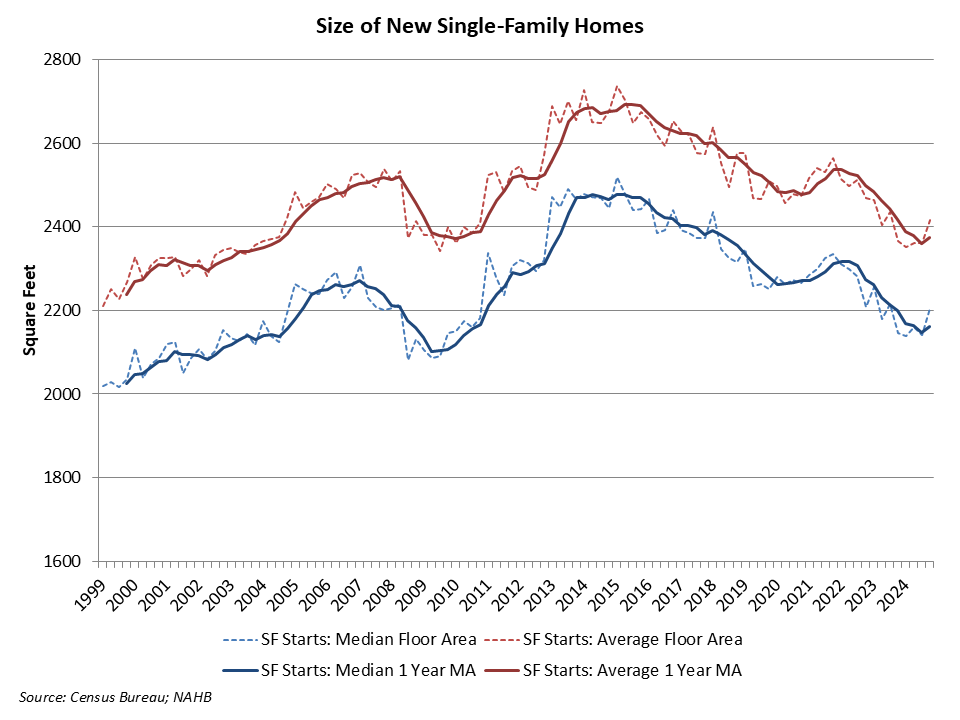
Eric Lynch2025-04-14T08:19:20-05:00The most common sources for products used in home building and remodeling are specialty retailers, lumber yards, and wholesale distributors, according to two recent NAHB surveys. The surveys include one of single-family homebuilders in the October 2024 NAHB/Wells Fargo Housing Market Index (HMI) and one of remodelers in the Q3 2024 NAHB/Westlake Royal Remodeling Market Index (RMI). Both surveys asked respondents where they purchase building products, regardless of who ultimately purchases them (themselves or subcontractors) When averaging across 24 building product categories, the top three major channels of distribution are roughly the same for both builders and remodelers. Specialty retailers, lumber yards, and wholesale distributors together account for around 70% of building product purchases. When analyzing the specific products purchased at lumber yards, the top products purchased by both builders and remodelers were basic lumber products including plywood & OSB, sawn lumber, and engineered lumber & I-joists. One major difference between builders and remodelers was the share of those who purchase products from home improvement centers. Remodelers are three times as likely to buy products at this channel of distribution compared to builders. Nevertheless, one specific product category, hand & power tools, is purchased at home improvement centers by a majority of both remodelers (68%) and builders (56%). Of those that do purchase hand & power tools at home improvement centers, 11% of remodelers purchased at least one other product there compared to 3% of builders. A subsequent post on who is most often responsible for choosing these products will come later. Please click here to be redirected to the full report. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.