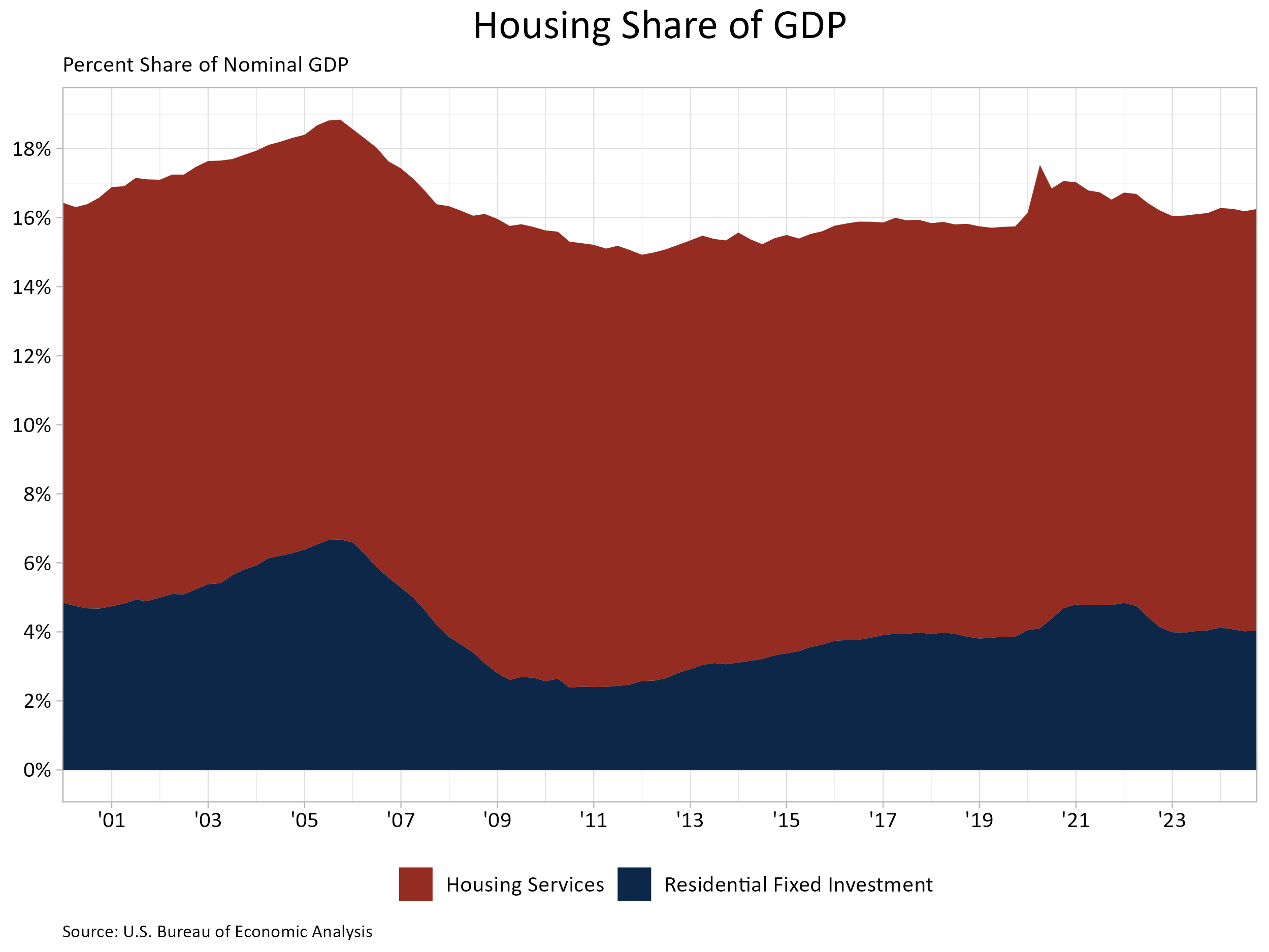
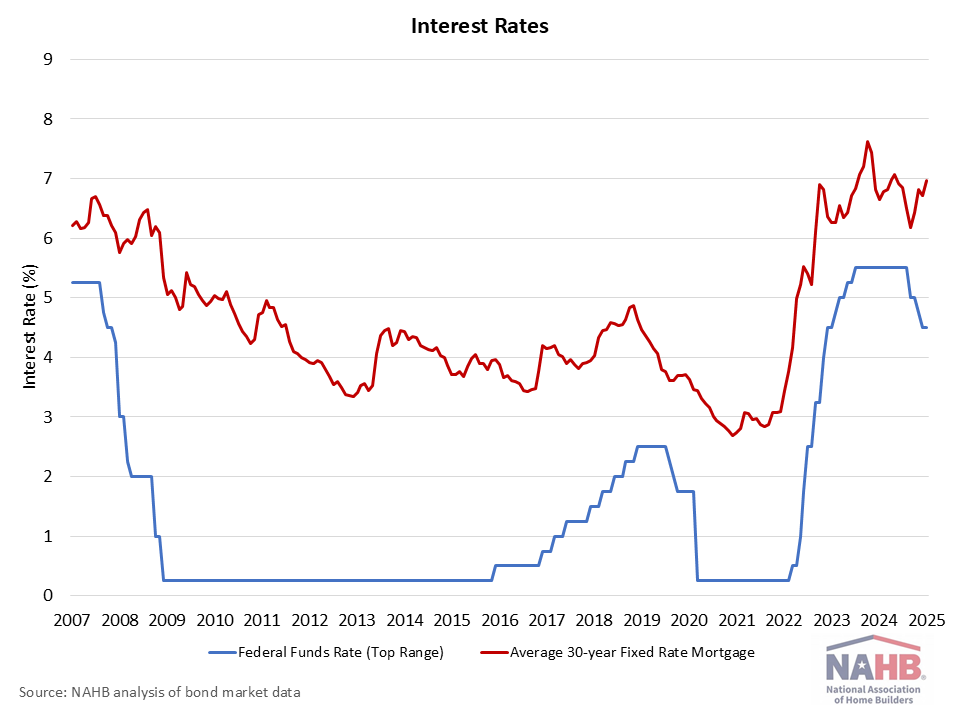
NAHB Urges Building Material Exemption from Planned Tariffs Against Canada and Mexico
Diana Carroll2025-01-31T13:18:26-06:00With President Trump announcing that he plans to impose 25% tariffs on Canadian and Mexican goods coming into the United States, NAHB is urging the president to exempt building materials from the proposed tariffs because of their harmful effect on housing affordability.